
I will recommend reading the below post for libpcap & tcpdump packet analysis. System Libraries used by iftop command are as below. The main reason why i mentioned " ps" and " top" command is the fact that iftop command is very much analogous to the very famous " top" command, with the only difference that iftop command gives you a complete network usage statistics instead of process. Another such tool with a more interactive interface for process monitoring is " top". This command outputs the process table and complete details of all the process running on a Linux system. One heavily used command in Linux by all system administrators is the "ps" command. Network Bandwidth Monitoring in Linux with Iftop command The tools that we will be discussing in the posts are:

The information that's made available to the user by these tools are as below. The tools discussed in this post presents various important pieces of information about the traffic send and received by the network interfaces in Linux,which can be very useful in finding bottlenecks in network bandwidth. We will be discussing two such tools in this post. There are pretty good number of open source tools available for Linux, that does this job. However monitoring traffic (both outgoing and incoming) on a Linux machine becomes a priority during crisis. Use the below command to check only send/receive data.Analyzing and monitoring network traffic of an entire network infrastructure can be done by plotting graphs based on any RRD tool. Sample outputs: -total-cpu-usage-dsk/total-net/total-paging– -system– If you use only dstat command it will give you complete information like total-CPU-usage, dsk/total, net/total, paging etc. You can check “man page” for various alternatives. You can utilize the choice to indicate different values with different colors. It will indicate details in exactly with the same time period. dstat give you subtle elements in sections and unmistakably appears in what size and unit are shown. $ ifstat -t -i eth0ĭstat is an adaptable asset insights tool. – t give the time and – I is used to mentioning ethernet. We have utilized “- t” and “- I” alternative with ifstat command. Use beneath command of ifstat which gives you bandwidth with subtle elements of Time, information move In/Out and so forth.
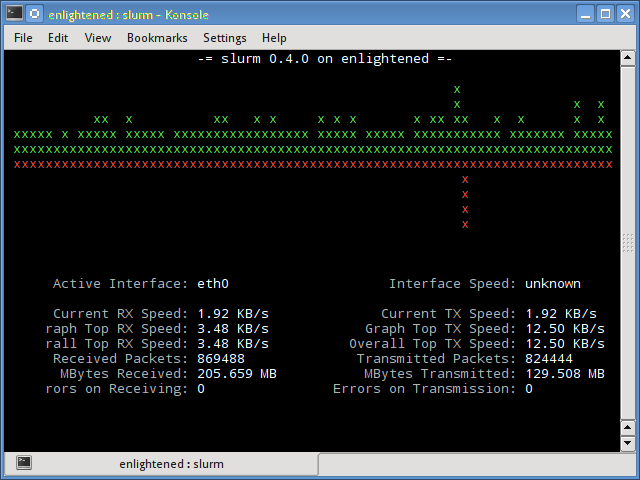
Ifstat give network usage in group style mode. If you want the current status of network usage then run below command with some options. Attempt this command after some time so the vnstat will assemble a few subtle elements identified with network usage. When you run this vnstat first time it will give you notice message “ eth3: Not enough data available yet“. You can be checked the historical backdrop of system bandwidth utilization with the usage of vnstat. Continue putting away the extent of information exchange constantly. It will keep running as a background process or daemon. Vnstat is an alternate tool from different tools. You can also use the “d” option to get extra network details. you can pick ethernet alternative by up/down arrow to check bandwidth on the graph. The output of bmon tool additionally gives a diagram and packet details. bmon (Bandwidth Monitoring) is another apparatus to monitor bandwidth on a Linux machine.
#Linux bandwidth monitoring tool install#
$ apt-get install nloadīmon is like nload but bmon will give you some more detail.

In the event that you need to investigate incoming/outgoing traffic then nload will be the great choice. Nload is easy to use and no any other supported options are available. Nload is a command line tool which is used to monitor network bandwidth of incoming and outgoing traffic. These commands will monitor network transfer speed and bandwidth of all incoming and outgoing traffic. These are the best commands to get a quick look about your network utilization. I will share a few commands which will give you the points of interest of Network transmission capacity utilization. This article depends on Network Monitoring.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
